Glue Ear
What is glue ear?
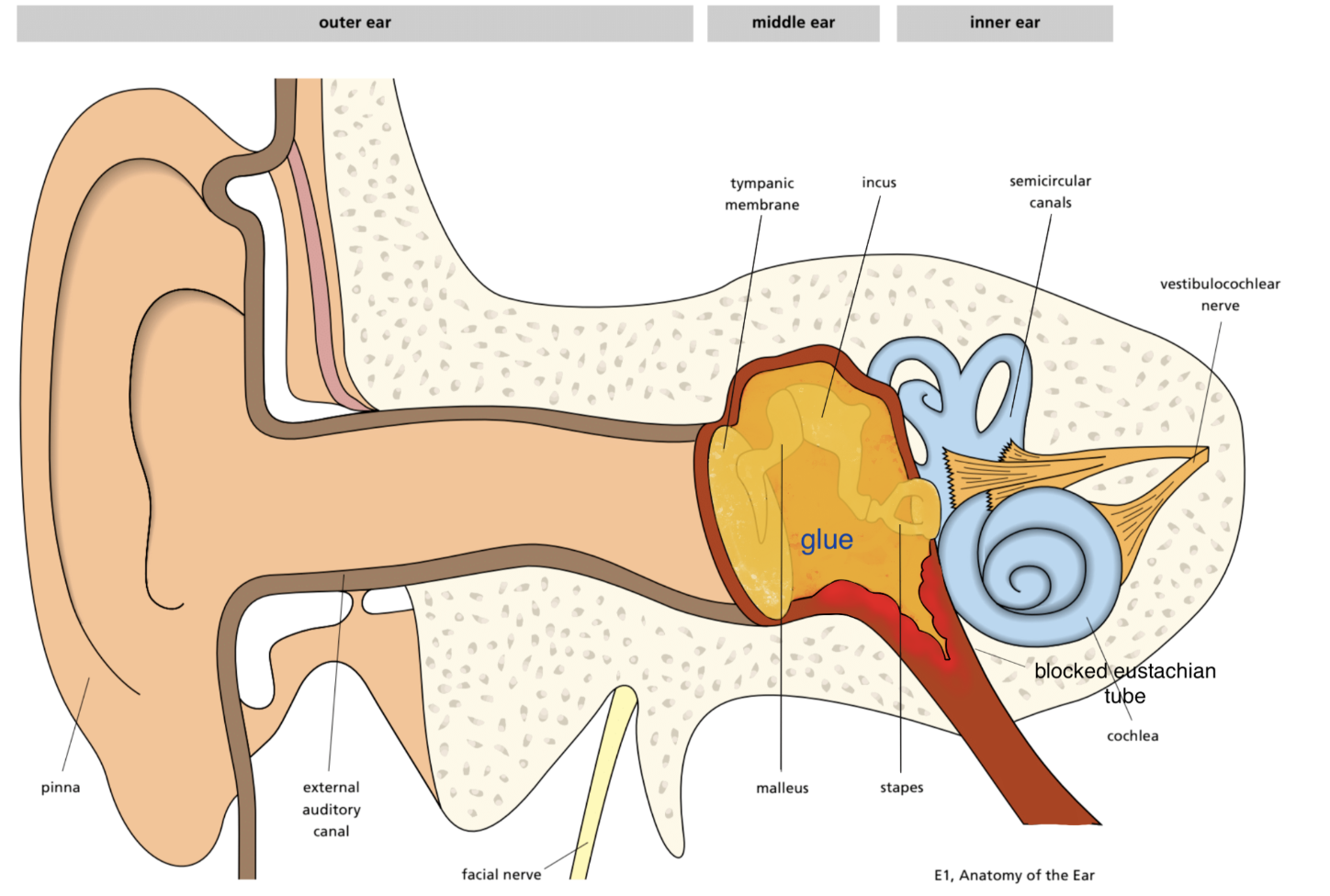
Glue ear is an accumulation of fluid within the middle ear that can lead to hearing loss.
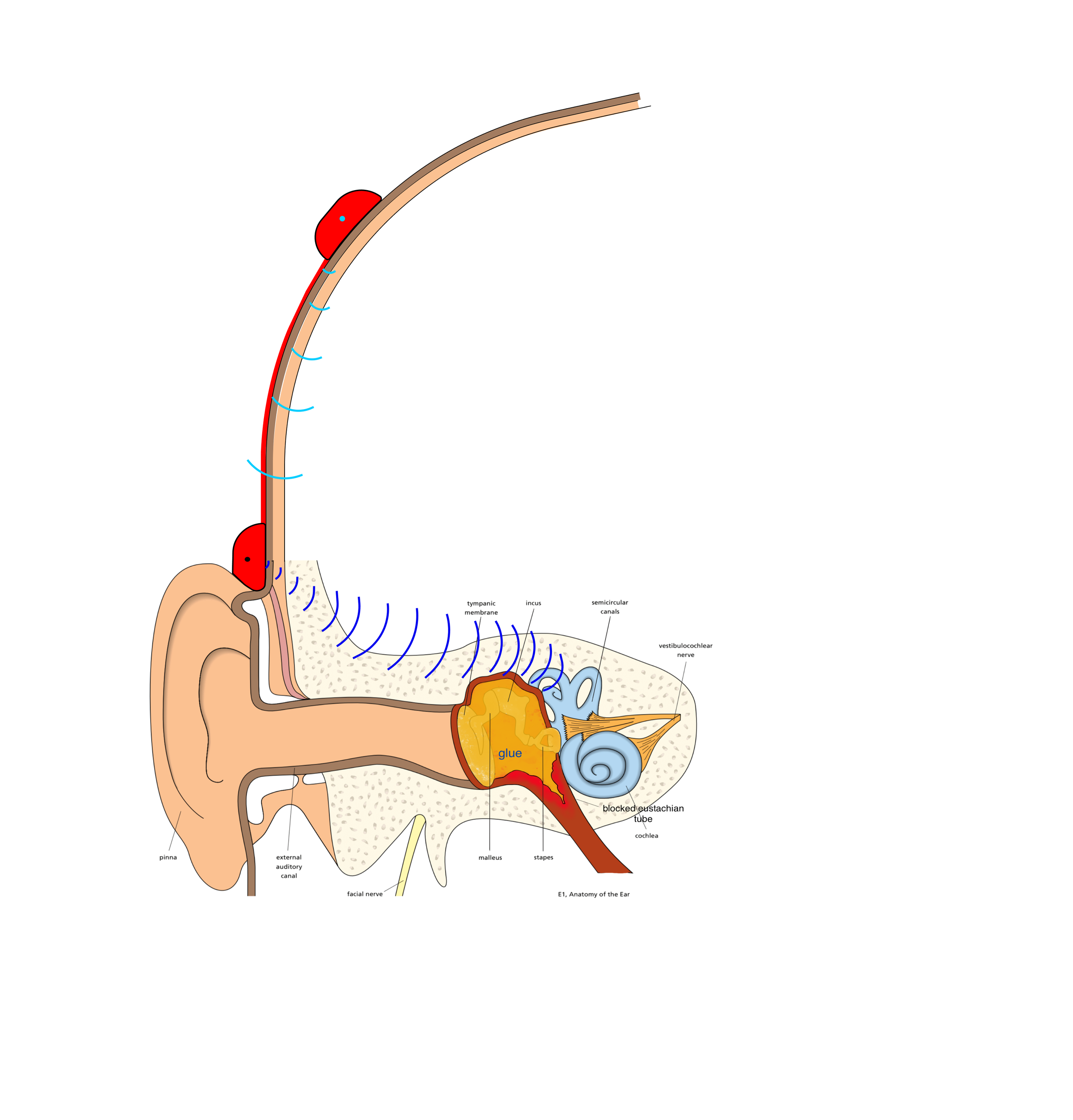
The middle ear is the space where sound is transmitted from the eardrum to the inner ear. The presence of fluid in this cavity impedes the transmission of sound.
The consistency of the fluid is usually thick and viscous, like “snot,” hence the term "glue". The fluid is produced by mucous glands in the middle ear and is essentially similar to the mucus that is produced in the nose.
The condition is very common in children from the ages of 2 to 5 and occurs mostly in the winter.
An ear infection or a cold may precipitate the development of glue ear and in most children the glue ear resolves within a few weeks after onset.It may cause a and cause a hearing impairment and in some children it may persist. Occasionally it can cause children to become off balance and clumsy. Generally if it is present for more than 3 to 4 months it is likely to persist particularly in the winter season.
How can glue ear affect my child?
Glue ear can affect children by causing a hearing loss. In younger children (around 2-3 years old) there may be an impact on speech development. Parents may notice that their child’s speech is not so clear and that they may miss the beginnings and ends of words and mix up certain consonants such as "b" and "d."
Behavioural issues can also occur, with children becoming easily frustrated and tired, "losing it" and withdrawing from larger groups of children.
School teachers may notice that children may be easily distracted and have trouble following instructions especially in group situations such as in swimming classes. Some children experience loudness intolerance particularly with the hoover and hairdryers.
What can you do about glue ear
Treatment options will depend on the degree and impact of the hearing loss and not all children need treatment.
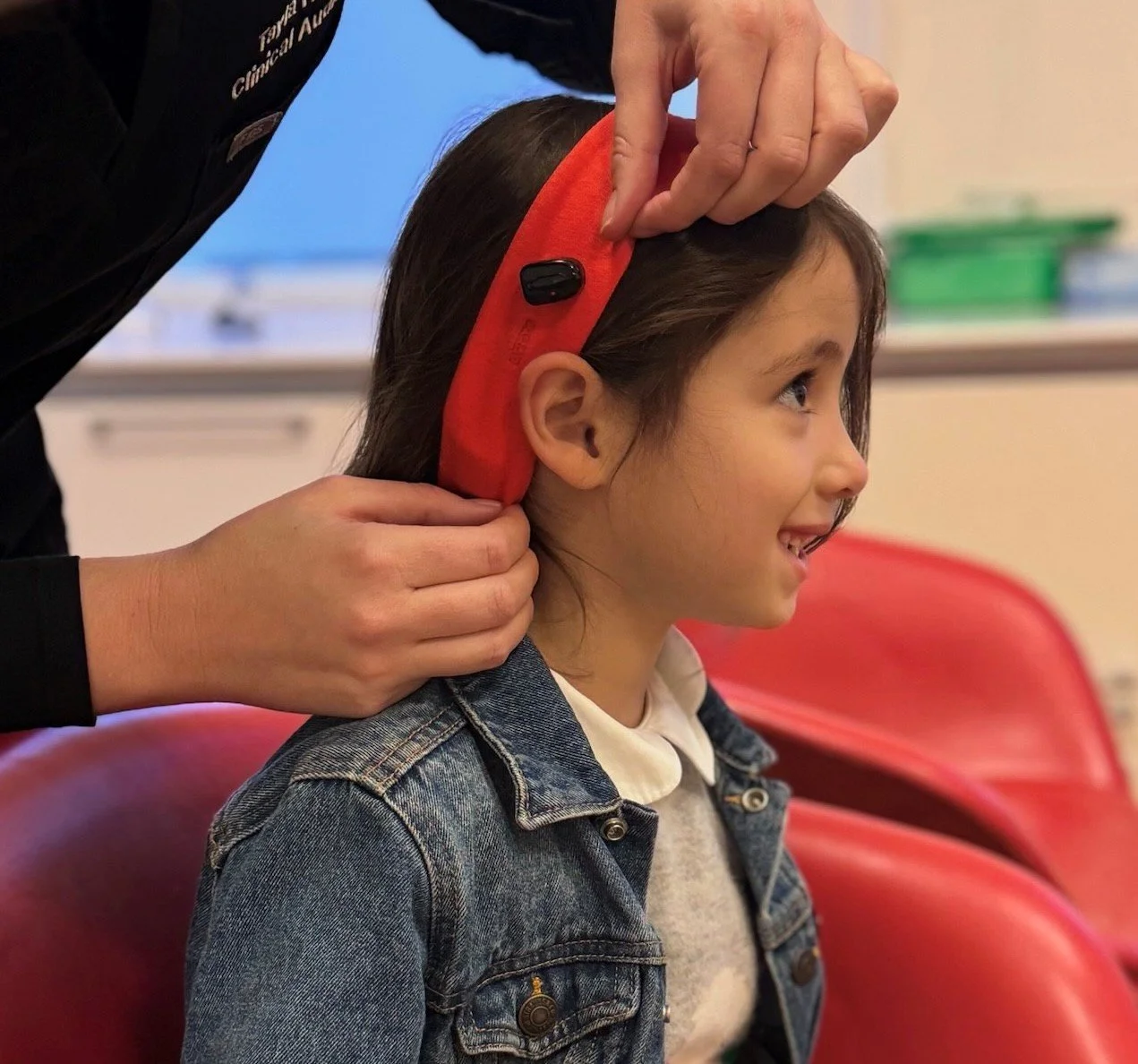
Softband hearing aids are an easy non interventional management option to help children with glue ear hear. They work by having a hearing aid secured in a pocket iwithn the band that transmits sound through the bone. They are surprisingly well received by children and can be fitted with days after the diagnosis.
The Otovent device is a balloon that is inflated by blowing through one nostril and this in turn attempts to open the eustachian tube with positive pressure. This can be challenging for younger children and generally only possible in children >4 years.
The use of long term antibiotics and nasal steroids has not been shown to be effective and is not recommended
Grommet insertion
A grommet is a plastic tube that is placed across the tympanic membrane to allow ventilation of the middle ear. This is the most definitive treatment for glue ear but requires a small operation under general anaesthetic